
- Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture manual#
- Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture password#
- Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture Pc#
- Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture windows#
Using the manual pages available with the Linux operating system, you read or search through the manual pages for options for selecting the desired information from the pcap file. Note: You may need to press ENTER to see the prompt.

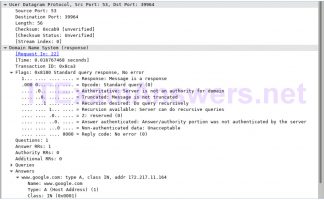
What is the relative sequence number set to? Well-known, registered (HTTP or web protocol) How would you classify the destination port? In this example, the source port is 58716.
Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture windows#
Note : You may have to adjust the top and middle windows sizes within Wireshark to display the necessary information.Īnswers will vary. Locate the flag that is set in this packet.
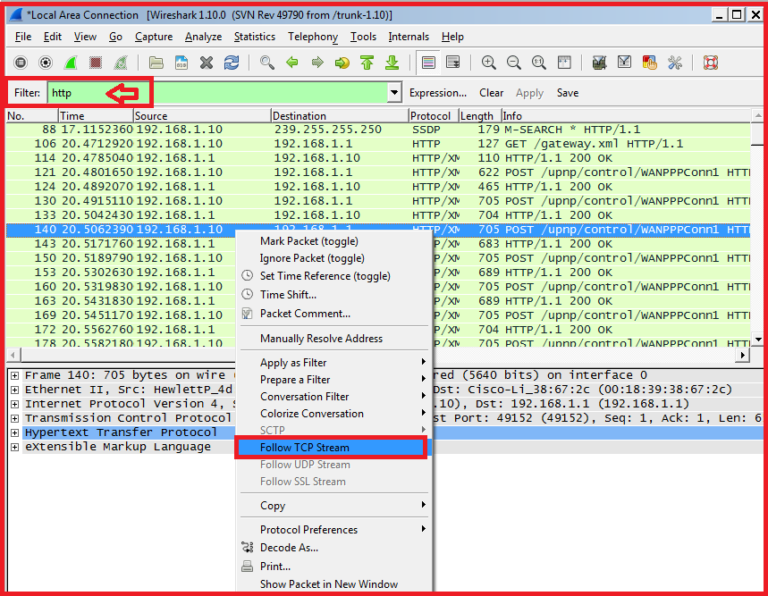
Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture Pc#
In this example, frame 1 is the start of the three-way handshake between the PC and the server on H4.Step 2: Examine the information within packets including IP addresses, TCP port numbers, and TCP control flags. In this example, the first 3 frames are the interested traffic. Select the saved pcap file located at /home/analyst/capture.pcap. Click OK when prompted by the warning regarding running Wireshark as superuser. Part 2: Analyze the Packets using Wireshark Step 1: Apply a filter to the saved capture. After the tcpdump starts, quickly navigate to 172.16.0.40 in the Firefox web browser.$ sudo tcpdump – i H1-eth0 -v -c 50 -w /home/analyst/ capture.pcap This capture will stop after capturing 50 packets, as it is configured with the option -c 50. With the -v option, you can watch the progress. After the Firefox window opens, start a tcpdump session in the terminal Node: H1 and send the output to a file called capture.pcap.On host H1, use the switch user command to switch from the root user to the analyst user account: For security purposes, you are not able to run Firefox from the root user account.analyst]# /home/analyst/ /scripts/ reg_server_start.sh
Using wireshark to examine a udp dns capture password#
Log in with username analyst and the password cyberops. Instructions Part 1: Prepare the Hosts to Capture the Traffic

If using a packet sniffer is an issue, the instructor may wish to assign the lab as homework or perform a walk-through demonstration. It is recommended that permission be obtained before running Wireshark for this lab. A PC can have multiple, simultaneous, active TCP sessions with various web sites.Īnswers Note : Using a packet sniffer, such as Wireshark, may be considered a breach of the security policy of the school. For example, when a PC uses a web browser to surf the internet, a three-way handshake is initiated, and a session is established between the PC host and web server. When an application, such as HTTP or File Transfer Protocol (FTP) first starts on a host, TCP uses the three-way handshake to establish a reliable TCP session between the two hosts. In this lab, you will use Wireshark to capture and examine packets generated between the PC browser using the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and a web server, such as. Part 3: View the Packets using tcpdump Background / Scenario Part 2: Analyze the Packets using Wireshark Part 1: Prepare the Hosts to Capture the Traffic Lab – Using Wireshark to Observe the TCP 3-Way Handshake (Answers Version)Īnswers Note : Red font color or g ray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
